Cervical osteosarcoma is a condition that more often than other conditions becomes the cause of neck pain. It is important to diagnose the disease at the right time and begin treatment, among other things, including neck gymnastics to treat osteonecrosis. It will help strengthen the muscle corset, form correct posture and prevent the development of possible complications.
Diagnosis and treatment of cervical osteonecrosis
People can suspect the development of the disease in themselves by the manifestation of pain, discomfort in the neck area, more intense when turning, tilting the head, in prolonged uncomfortable position, hypothermia. It is important to distinguish degenerative osteopathy of the cervical spine from entrapment neuropathy of the median nerve. Experts of the medical university believe that in 48. 5% of cases, the diagnosis is made incorrectly.
In terms of treatment, the highest effectiveness is shown through probiotics combined with special therapeutic and recreational exercises. Such a conclusion was reached by scientists who published the results of their study in the Journal of Georgian Medical News.
Physical therapy exercises for the neck
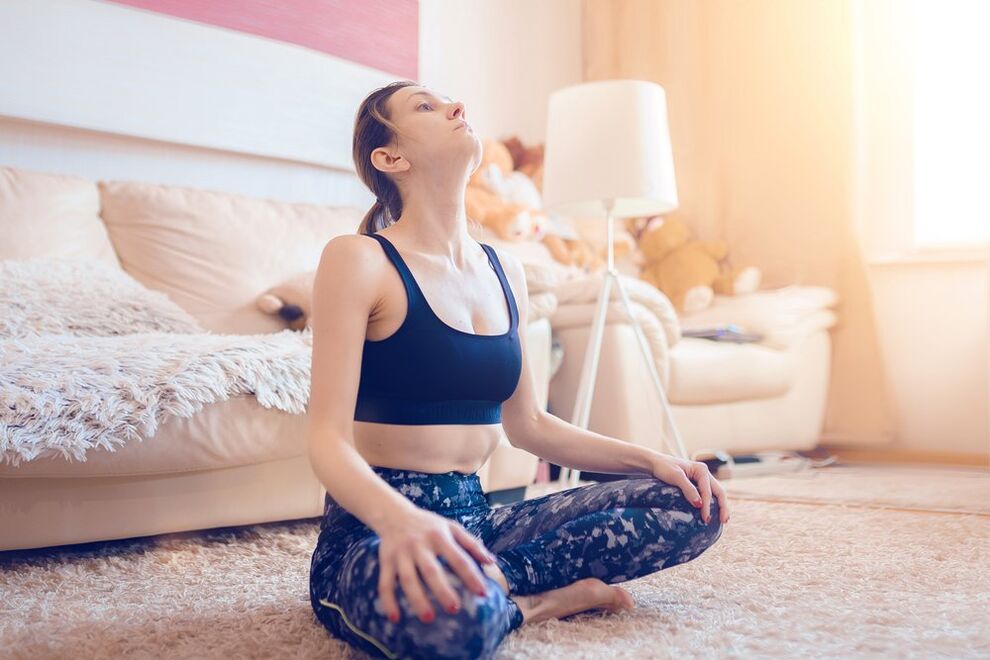

Physical therapy for cervical osteochondrosis includes the following exercises:
- Tilt head. Stand up straight or sit in a chair with your back straight. Slowly tilt your head toward your right shoulder, feeling the tension in your neck muscles. Stay motionless in this position for a few seconds and perform the exercise in the other direction, i. e. leaning towards the opposite shoulder.
- Turning. With your head down, try to touch the depression with your chin - the pit. To enhance the effect, you can make an impact on the back of the head with diagonal strokes. Hold at the point of highest tension for a few seconds, then start turning your head - first in one direction, sliding your chin along the top of your sternum, then in the other.
- Raise and lower the shoulders. Stand straight with your arms at your sides and begin to raise and lower your shoulders. To increase efficiency, you can increase the load and small dumbbells will help with this. Alternatively, you can fill a plastic bottle with water or sand.
- Circular motion with shoulders. This exercise is very similar to the previous one. The only difference is that the shoulders do not need to be raised and lowered, but performed in a circular motion. Keep your back straight.
- Prolonged. Stand up straight or sit in a chair with your back straight. Place your crossed arms at the back of your head. Tilt your head back, and at the same time use your hands to create resistance. Measure at the highest voltage point in seconds.
- Flexibility. This is similar to the previous exercise, only it is done in the opposite direction. It is necessary to place both hands crossed on the forehead and begin to lower the head, supporting the hands. Measure at the point of highest voltage for a few seconds.
Exercises must be performed rhythmically, quickly, at the right time with the breath. If severe pain or other unpleasant sensations appear, interrupt classes and consult a doctor about this.





































